Waves are a fundamental aspect of the physical world, occurring in various forms, from the waves in the ocean to the vibrations of sound in the air. A mechanical wave is one of the two primary categories of waves which require a medium to travel through. There are two types of mechanical waves: longitudinal and transverse waves. Understanding the characteristics and behaviours of these waves is essential to many areas of science and technology. This blog post will explore the characteristics of these waves, their differences, and their applications.
What are Mechanical Waves?
Mechanical waves are a type of wave that needs a medium to travel through. In other words, they require a substance to propagate. The energy of the mechanical waves moves through the medium in which it travels, causing it to vibrate. A mechanical wave can be characterised by its amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and velocity. Many types of mechanical waves are mentioned below.
Longitudinal Waves
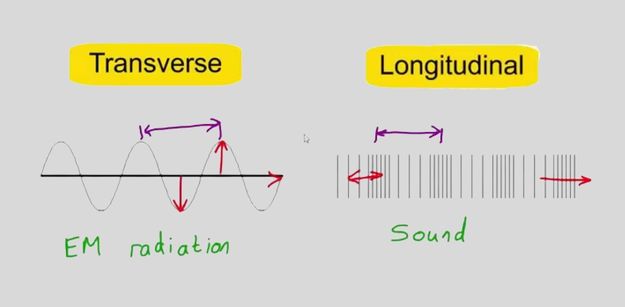
Longitudinal waves, also known as compression waves, are waves in which the disturbance or displacement is in the same direction as the wave’s travel direction. In a longitudinal wave, the medium moves back and forth parallel to the direction of the wave’s motion. Sound waves are a typical example of longitudinal waves. When a sound wave travels through the air, it creates high and low-pressure regions, which vibrate the air molecules. The areas of high pressure are known as compressions, and the areas of low pressure are known as rarefactions.
Transverse Waves Transverse waves, also known as shear waves, are waves in which the disturbance or displacement is perpendicular to the direction of the wave’s motion. In a transverse wave, the medium moves up and down or side to side. Light waves and electromagnetic waves are examples of transverse waves. When a light wave travels through space, it creates disturbances in the electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to the direction of travel.
Longitudinal vs Transverse Waves: The Difference
The primary difference between longitudinal and transverse waves is the direction of the disturbance relative to the direction of travel. In longitudinal waves, the disturbance is parallel to the direction of travel, whereas in transverse waves, the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of travel. Another difference is that longitudinal waves require a compressible medium, while transverse waves can travel through a non-compressible medium, such as a solid. Finally, the speed of a transverse wave is typically faster than that of a longitudinal wave.
Applications of Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Both longitudinal and transverse waves have many practical applications in various fields of science and technology. Longitudinal waves are used in medical ultrasound imaging, which uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the body’s internal structures. Transverse waves are used in many applications, such as fibre optic communication systems, where light waves transmit data over long distances. They are also used in the entertainment industry, such as in laser light shows, utilising transverse light waves to create stunning visual effects.
In conclusion, studying a mechanical wave is crucial to many fields of science and technology. By understanding the characteristics and behaviours of types of mechanical waves, you can better understand the physical world and develop new technologies that utilise these waves. Whether it’s medical imaging or fibre optic communication, the practical applications of these waves are diverse and far-reaching. Our understanding of mechanical waves will grow and expand as we continue exploring the world around us.